
Effect of an indigenous preparation Liv.52 on Hepatitis B Antigen-Carriage
Kelkar, S.S., M.D., Prof. of Microbiology, Grant Medical College, Bombay and Mahajan, R.K., Lecturer in
Microbiology, Medical College, Aurangabad., India.
| RESULTS The results of the present study indicate that Liv.52 has a dramatic effect in reducing the SGOT and SGPT levels. In all the five carriers the enzyme levels monitored for about two years prior to treatment had shown consistent and persistently-raised levels for both SGOT and SGPT. With therapy each carrier showed a fall in the enzyme levels and, in three, the enzyme levels came down to normal values. The reasonable inference was that Liv.52 protected the hepatocyte from damage by the proliferating hepatitis B virus. The mode of action was not due to virus destruction because there was no change in the quantity of virus antigen in any of the five carriers. Since there was no fundamental change in the host-parasitic relationship between the hepatitis B virus and the host-carrier, it appears possible that the drug exerted a trophic or protective influence on the hepatocyte, possibly by way of providing essential metabolites which prevented death of the liver cells. Like other preparations of indigenous origin, Liv.52 appears to hold out promise where currently-available remedies are ineffective. |
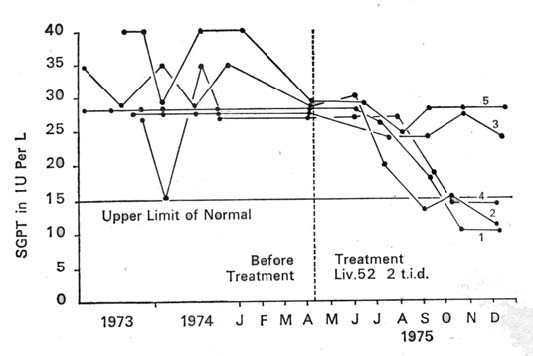 |
| Graph III: Effect of Liv.52 on SGPT levels in five symptomless carriers of HBs Ag. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are grateful to The Himalaya Drug Co., for providing supplies of Liv.52 tablets used in this study.
REFERENCES
1. Aron, E. and Maupas, P., Stimulation of Australia-antigen production. Lancet (1973) : 1, 438.
2. Dasgupta, M. and Mukerjee, A.B., Chronic active hepatitis. J. Ind. Med. Prof. (1971) : 18, 8097.
3. Dejanor, I.I., Trajkovski, B., Solerovska, L. and Ranic, P., Australia-antigen and antibody in 14,379 volunteer blood donors from S.R. Macedonia (Yugoslavia). Lancet (1971) : 2, 164.
4. Gioannini, P., Scalise, G., Delia, S., Bird, R.G. and Zuckerman, A.J., Heterologous stimulation of hepatitis B antigen. Lancet (1974) : 2, 651.
5. Jaffari, S.M.H. and Raj, S., Liv.52 in infective hepatitis. Antiseptic (1969) : 5, 353.
6. Joglekar, G.V., Chitale, G.K. and Balwani, J.H., Protection by indigenous drugs against hepatotoxic effects of carbon tetrachloride in mice. Acta pharmacol. et toxicol. (1963) : 20, 73.
7. Karve, S.R., Niphadkar, K.B. and Kelkar, S.S., Australia antigen in professional blood donors and student volunteers at Poona. Ind. J. Med. Sci. (1973) : 27, 521.
8. Kelkar, S.S., Karhade, N.V. and Bhagwat, R.B., Australia (hepatitis associated) antigen in cirrhosis of the liver at Aurangabad. Ind. J. Med. Res. (1973) : 61, 1614.
9. Kelkar, S.S., Karhade, N.V. and Kotwal, S.E., Haemolytic complement, anti-complementary activity and hepatitis B antigen in sera of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Ind. J. Med. Res. (1975) : 63, 41.
10. Kelkar, S.S., Niphadkar, K.B. and Khare, P.M., Immunoelectrphoresis (counterimmunoelectro-phoresis) for detection of the Australia antigen. Med. J. Western India (1972) : 5, 18.
11. Kelkar, S.S., Sharma, K.D. and Patil, S.D., Australia (hepatitis-associated) antigen in blood donors at Aurangabad by the immunoelectroosmophoretic technique. Ind. J. Path. Bact. (1972) : 15, 99.
12. Lebacq, E., Liver disease in carriers of Australia-antigen. Lancet (1971) : 2, 977.
13. Mahajan, R.K. and Kelkar, S.S., Hepatitis B antigen-carriage in medical students. Maharashtra Med. J. (1976) : 23, 53.
14. Mehrotra, M.P. and Mathur, D.C., Liv.52 trial in infective hepatitis. Antiseptic (1973) : 70, 114.
15. Mukerjee, A.B. and Dasgupta, M., Treatment of viral hepatitis by an indigenous drug—Liv.52. Ind. Practit. (1970) : 6, 1357.
16. Reed, W.D., Eddleston, A. L.W.F., Cullens, H., Williams, R., Zuckerman, A.J. : Peters, D.K., Gwyn, W.D. and Maycock, W.D.A. 1973. Infusion of hepatitis B antibody in antigen-positive active chronic hepatitis. Lancet (1973) : 2, 1347.
17. Reitman, S. and Frankel, S. 1957. A colorimetric method for determination of serum glutamic oxaloacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Am. J. Clin. Path. (1957) : 28, 56.
18. Sama, S.K., Krishnamurthy, L. Ramachandran, K. and Lal, K., Efficacy of an indigenous compound preparation Liv.52 in acute viral hepatitis-a double blind study. Ind. J. Med. Res. (1976) : 64, 738-741.
19. Sama, S.K., Wali, J.P. and Lal, K. 1974. Study of healthy H.A.A. carriers. Ind. J. Med. Res. (1974) : 62, 649.
20. Sherlock, S., Fox, R.A., Niazi, S.P. and Scheuer, P.J., 1970. Chronic liver disease and primary liver-cell cancer with hepatitis-associated (Australia) antigen in serum. Lancet (1970) : 1, 1243.
21. Shulman, N.R., Hepatitis-associated antigen. Am. J. med. (1970): 49, 669.
22. Singleton, J.W., Fitch, R.A., Merrill, D.A., Kohler, P.F. and Rettberg, W.A.H., Liver disease in Australia-antigen-positive blood-donors. Lancet (1971) : 2, 785.
23. Skinhoj, P., Hepatitis-associated antigen in hospital patients. Lancet (1971) : 1, 1301.
Refference:
http://www.himalayahealthcare.com/pdf_files/liv237.pdf

Copyrights © 2009 healthyliver.co.uk
